Abstract
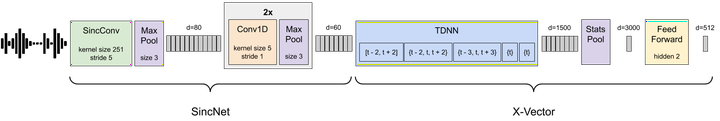
Despite the growing popularity of metric learning approaches, very little work has attempted to perform a fair comparison of these techniques for speaker verification. We try to fill this gap and compare several metric learning loss functions in a systematic manner on the VoxCeleb dataset. The first family of loss functions is derived from the cross entropy loss (usually used for supervised classification) and includes the congenerous cosine loss, the additive angular margin loss, and the center loss. The second family of loss functions focuses on the similarity between training samples and includes the contrastive loss and the triplet loss. We show that the additive angular margin loss function outperforms all other loss functions in the study, while learning more robust representations. Based on a combination of SincNet trainable features and the x-vector architecture, the network used in this paper brings us a step closer to a really-end-to-end speaker verification system, when combined with the additive angular margin loss, while still being competitive with the x-vector baseline. In the spirit of reproducible research, we also release open source Python code for reproducing our results, and share pretrained PyTorch models on torch.hub that can be used either directly or after fine-tuning.
Note
This paper was accepted at SLSP 2020.
Quick Usage
Apply our best pretrained model with just a couple lines of Python code:
import torch
model = torch.hub.load('pyannote/pyannote-audio', 'emb')
# extract embeddings
emb1 = model({'audio': '/path/to/file1.wav'})
emb2 = model({'audio': '/path/to/file2.wav'})
# compute distance between embeddings
from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist
import numpy as np
distance = np.mean(cdist(emb1, emb2, metric='cosine'))